Eye diseases that can be treated with laser eye surgery:
3 months Victor Derhartunian
Vision defects, also known as refractive errors, are not diseases in the classical sense, but anomalies in the refraction of light by the eye, which result in the light not being focused correctly on the retina.
Nevertheless, they can be subsumed as a deviation from the normal healthy state, so that they fall under the term “disease” in the broadest sense.
Accordingly, laser eye surgery is the most modern and effective treatment option for the following eye anomalies:
Short-sightedness (myopia)
Short-sightedness (myopia) is a vision defect in which nearby objects are seen clearly, while distant objects appear blurred.
It is caused by the shape of the eyeball being too long or the cornea being too curved, which causes light to focus in front of the retina.
Typical symptoms are blurred vision in the distance and frequent squinting of the eyes.
- With Femto-LASIK a thin corneal flap is precisely cut with a femtosecond laser.
The underlying tissue is then reshaped with an excimer laser to reduce the curvature of the cornea and focus the light correctly on the retina. - With Trans-PRK the top layer of the cornea is removed and the underlying layer is treated directly with an excimer laser.
Both procedures can significantly improve vision and reduce dependence on glasses or contact lenses.
Farsightedness (hyperopia)
Farsightedness (hyperopia) is a vision defect in which people see distant objects more clearly than near objects.
This is caused by the eyeball being too short or the cornea being flat, causing light to focus behind the retina.
Symptoms include blurred vision of close objects, headaches and eye fatigue, especially during activities such as reading or working at a computer.
Femto-LASIK and Trans-PRK are used in the same way as for short-sightedness.
Only the corneal ablation is adjusted so that the refraction of light is optimized so that you can also see clearly at close range again.
Astigmatism (curvature of the cornea)
Astigmatism is a vision defect in which the cornea or lens is unevenly curved.
These irregularities cause light rays to hit the retina at different angles, resulting in blurred or distorted vision.
Typical symptoms include blurred vision, headaches and eye fatigue, especially after intense visual exertion.
Presbyopia (presbyopia)
Presbyopia, also known as presbyopia, is an age-related visual defect in which the eye’s ability to see close objects in focus gradually decreases.
This change usually occurs from the age of 40 and is caused by a stiffening of the lens and the loss of its elasticity.
Typical symptoms include difficulty reading small print or focusing on close objects, which often leads to headaches and eye strain.
PresbyMAX with excimer laser
PresbyMAX is a special laser eye procedure that was developed to correct presbyopia.
This procedure uses excimer laser technology to shape the cornea in such a way that it enables sharp vision both near and far.
PresbyMAX uses a multifocal approach in which the laser shapes different areas of the cornea differently to create multiple focal points.
This allows the eye to focus on objects at different distances.
The central area of the cornea is corrected for near vision, while the peripheral areas are adjusted for distance vision.
Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disease in which the cornea gradually thins and takes on a conical shape.
This leads to distorted and blurred vision.
The exact causes are not yet fully understood, but genetic and environmental factors such as excessive eye rubbing may play a role.
Typical symptoms include blurred vision, increased sensitivity to light and difficulty focusing.
Crosslinking instead of Femto-LASIK & Trans-PRK
Femto-LASIK and Trans-PRK are not the primary treatment options for keratoconus, as these procedures could further destabilize the already weakened cornea.
Instead, the Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL)-procedure is used to strengthen the cornea and stop the progression of the disease.
- Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL)In this procedure, the cornea is soaked with riboflavin (vitamin B2) and then irradiated with UV light.
This strengthens the cross-links between the collagen fibers of the cornea and increases its stability. - Laser-assisted methodsIn some cases, a combination of cross-linking and other laser-based methods can be used to smooth the corneal surface to improve the quality of vision.
This treatment can stop the progression of keratoconus and in some cases improve the quality of vision, but a complete cure of the structural changes is not always possible.
Diseases that cannot be treated with laser eye surgery
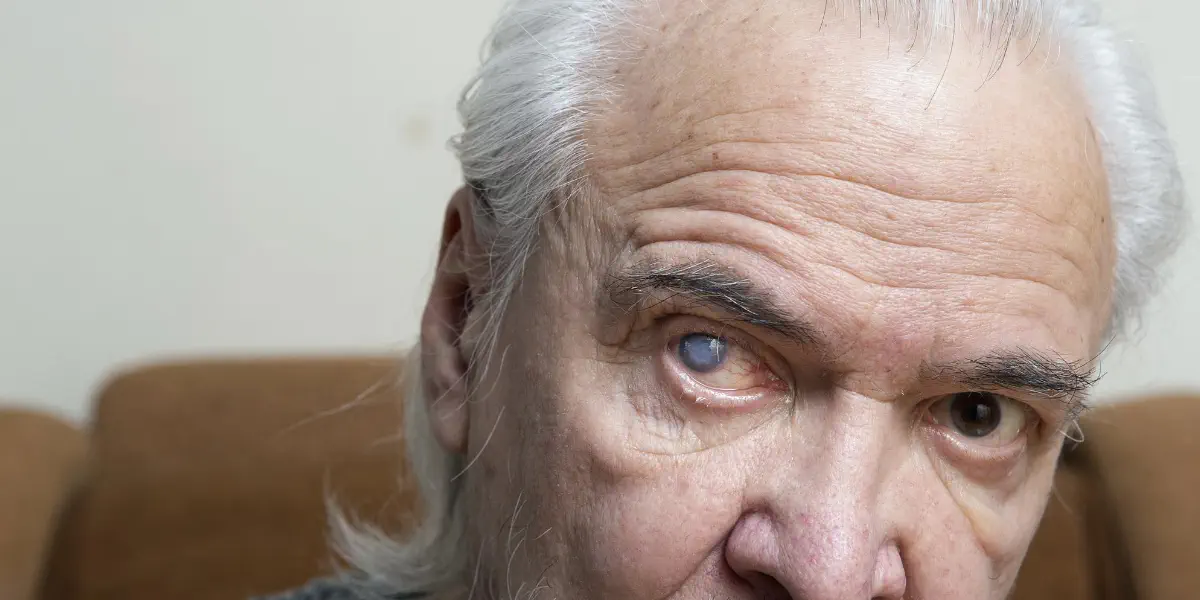

Cataracts – lens surgery instead of laser eye surgery
Cataracts, also known as cataracts, are a clouding of the natural lens of the eye that leads to blurred vision.
This condition often occurs with age, but can also be caused by injury or other conditions such as diabetes.
Typical symptoms include blurred vision, sensitivity to glare, impaired night vision and a progressive loss of visual acuity.
As cataracts cannot be treated with laser eye surgery, the most common and effective treatment method is cataract surgery.
During this procedure, the clouded lens is removed and replaced with a clear artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
If the natural lens is replaced by a multifocal lens, other visual defects can also be “corrected”.
It is then no longer necessary to wear glasses or contact lenses.
Glaucoma / glaucoma
Glaucoma, also known as glaucoma, is a group of eye diseases that can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss or blindness.
It is often caused by increased intraocular pressure that damages the optic nerve over time.
Typical symptoms include a gradual loss of peripheral vision, tunnel vision, and in advanced stages, blurred vision and blind spots in the field of vision.
As glaucoma cannot be treated by laser eye surgery alone, the alternative treatment options include
- MedicationEye drops and oral medications that lower intraocular pressure.
- Laser treatmentsProcedures such as selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT) and argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) can improve the drainage of ocular fluid and reduce pressure.
- SurgeryIn advanced cases, surgical interventions such as trabeculectomy or the use of drainage implants may be necessary to permanently reduce intraocular pressure.
Macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a chronic eye disease that affects the central part of the retina, the macula, and leads to a progressive loss of central vision.
This disease typically occurs in old age and can occur in two forms: dry and wet AMD.
Causes include genetic factors, smoking and an unhealthy diet.
Symptoms include blurred or distorted vision, dark or blank spots in the central field of vision and difficulty recognizing faces or reading.
- Dry AMD:
- Lifestyle changesA balanced diet, rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, can slow down the progression.
- Vitamin supplementsCertain vitamin and mineral supplements (e.g. AREDS formula) can slow down the progression of the disease.
- Moist AMD:
- InjectionsAnti-VEGF drugs are injected directly into the eye to stop the growth of abnormal blood vessels and improve visual acuity.
- Laser therapyPhotodynamic therapy (PDT), which uses a light-sensitive agent to destroy abnormal blood vessels, can be used in certain cases.